Introduction
Multifetal pregnancy constitutes a common iatrogenic outcome of ovarian stimulation with fertility drugs and assisted reproductive technique, quadruple pregnancy is considered as very high-risk pregnancy due to potential complications with increased perinatal, neonatal and infant mortality rate.1, 2, 3 Multifetal pregnancy reduction is defined as first trimester or early second trimester procedure for reducing the total number of foetuses in multifetal pregnancy by one or more selective reduction foetus are chosen based on health status by ultrasonographyby foetus with abnormality or disease risk is chosen for reduction.4, 5 Reduction of quadruplets to twin pregnancy improves perinatal morbidity and mortality.6
Case Report
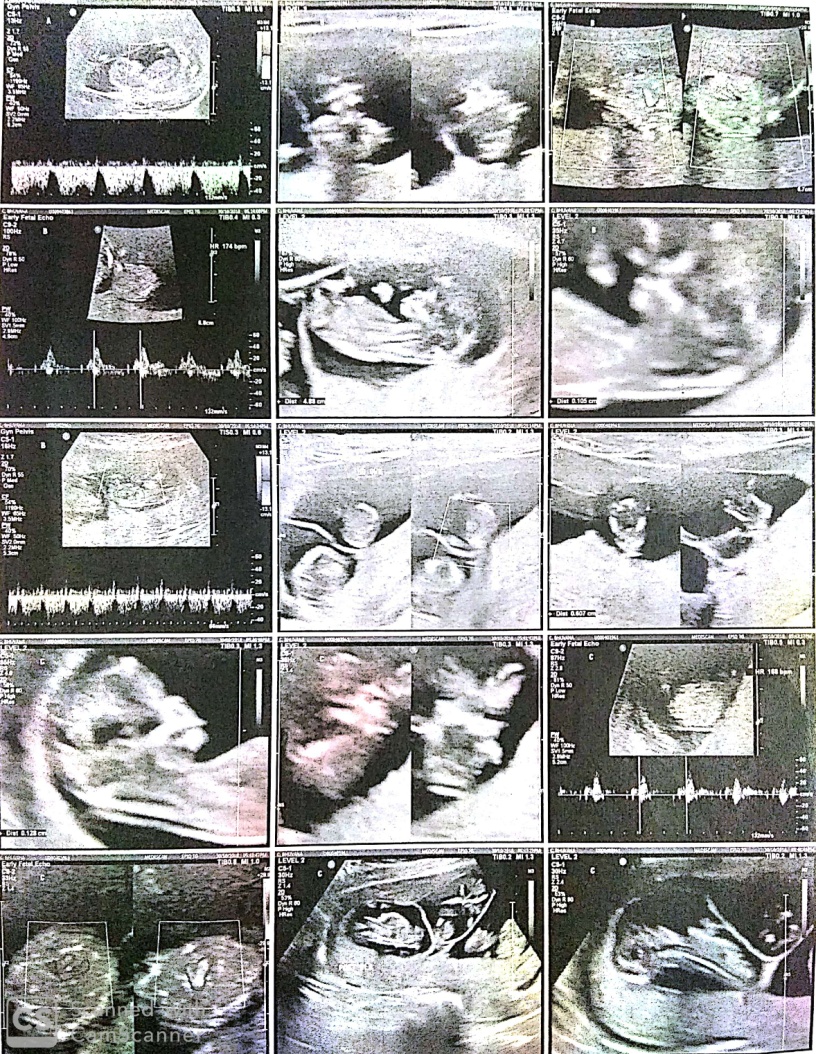
32 years old female was admitted in the department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology at Vinayaka Missions Medical College and Hospital, Karaikal, Pondicherry with obstetric score of G2 A1 conceived by IVF and resulted in quadruplet pregnancyFigure 1).
It was decided to reduce the fetuses to twin pregnancy at 10 weeks in view of the early pregnancy losses. Selective fetal reduction was carried out trans vaginally under ultrasound guidance using potassium chloride (KCl) with a separate needle for each fetus.
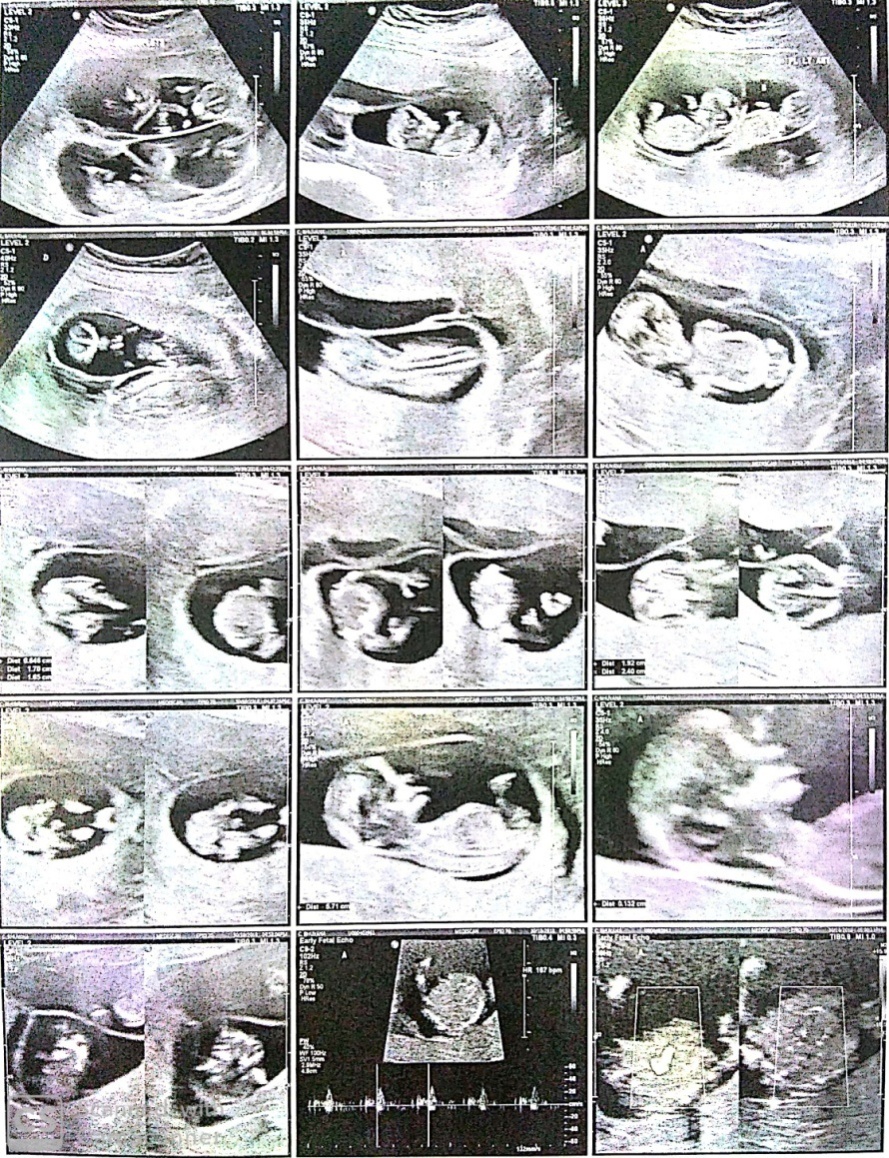
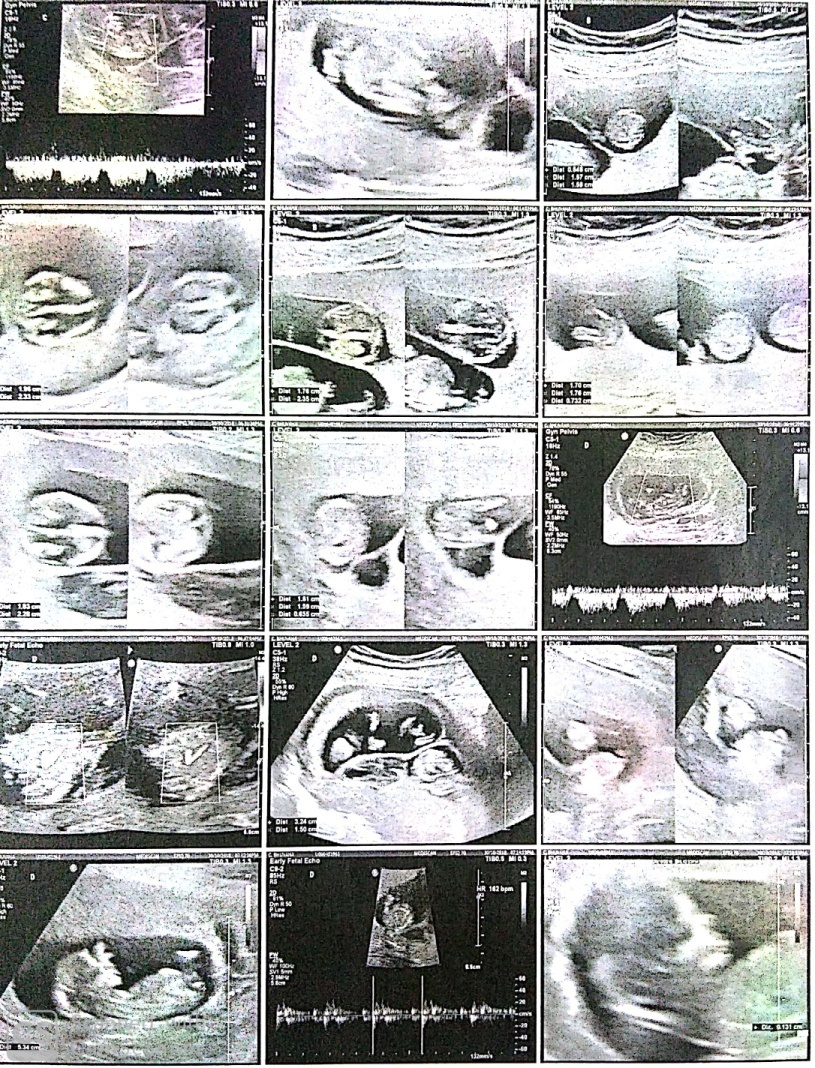
Under strict aseptic precautions, a 22G needle of 15cm was introduced under ultrasound guidance into the thoracic cavity of foetuses to be reduced. Two ml of KCl was injected into the thoraces of fetuses C and D. Cessation of fetal cardiac activity and movements were noted in fetuses C and D. Post reduction, other two foetuses A & B showed normal cardiac activity and movements (Figure 3). A reconfirmation of absent cardiac activity in the reduced fetuses and presence of cardiac activity in other two foetuses was done after 3 hours (Figure 2). Patient is advised to take rest for next 24 hours. Repeat scan was done at 22 weeks of gestation and was normal (Figure 4). The pregnancy was uneventful. In third trimester at 35 weeks of gestation, she presented with complaints of leaking per vaginum and pain in lower abdomen, underwent emergency LSCS (indication being PPROM with twin breech) delivered first baby as breech and second baby as vertex. Birth weight of first twin (girl baby) 1.7 kg and second twin (boy baby) 1.6 kg respectively. The APGAR scores of first-born twin were 6/10 at 5 min and 8/10 at 10 min and APGAR scores for second born twin were 8/10 at 5 min and 9/10 at 10 min. Both infants were admitted to neonatology department because of low birth weight for 10 days for observation.
Discussion
The incidence of multifetal pregnancies may be as high as 8% of all pregnancies resulting from use of ovulation induction drugs and as high as 53% after the use of gonadotropin.7 Invitro fertilisation and embryo transfer also increase the incidence of multifetal pregnancies upto 30%.8 In our case, patient was counselled about the risk of higher spontaneous abortions and preterm labour rates in multiple pregnancies and was offered the option of fetal reduction.9 The risks of procedure was explained to the patient and informed consent was obtained.10
Haiyan et al., reported a case of triplet pregnancy, during first trimester management options included fetal reduction of two twins by fetal intracardiac injection of KCl by ultrasound guided trans abdominal procedure.11 In our case the patient underwent ultrasound study that confirmed viability of all four foetuses with quadri chorionic quadri amniotic quadrupulet gestation. We performed quadruplet pregnancy foetal reduction through transvaginal ultrasound guided injection of KCl into thoraces of both foetuses C and D. Cessation of fetal cardiac activity and movements were noted infetuses C and D.
Van de Mheen et al., showed that if fetal anomaly for chromosomal or structural malformation were suspected, the fetal reduction would be performed selectively on that fetus.12 If no fetal anomaly was suspected then the smallest sac or the sacproximal to the uterine fundus would be selected. Selective termination can be done when fetal reduction used for significant developmental abnormality between 12 and 14 weeks of gestation and was showed that success rates were higher with abdominal than vaginal approach.13
Fawaz et al., reported that compared with twin pregnancies triplet and quadrapulet gestation are more likely to be diagnosed with PPROM delivered at less than 29 weeks of gestation.14 The gestational age at delivery for quadruplets varied in different reports, ranging from 28 weeks to 31 weeks. Compared to the above, our case got delivered at 35 weeks of gestation with twin breech PPROM delivered by emergency LSCS.
Conclusion
High order multiple pregnancies are associated with increased incidence of pregnancy complications like abortions, pre-eclampsia, preterm delivery and fetal death.15 Fetal reduction is increasingly common in context of infertility treatments for multiple fetal pregnancies.16 Fetal reduction procedure improves perinatal outcomes.